In a digital world shaped by every search query, the google algorithm act as invisible architects of our online experience. From humble beginnings that simply matched keywords to today’s complex, AI-driven models, understanding what is the algorithm of Google and how google search algorithm works has never been more critical. In 2025 the google algorithm puts user intent and experience front and center by rewarding pages that clearly answer questions and keep content fresh. It now values how long people stay on a page and whether they find the information helpful enough to interact. At the same time, the algorithm of google search tracks real author credentials and trusts sites that offer genuine value. That means pages with clear, up-to-date advice will rank higher. If you run a blog, an online shop, or a big brand site, putting readers first pays off. Keep your content fresh and easy to use to get more visits and build trust.
How Google’s Core Updates Directly Impact Your Traffic and Revenue
When you ask Google a question, you expect the best answer to come first. For businesses and content creators this means more clicks, more leads and ultimately higher sales. In the UK 91 percent of adults use Google as their main search engine. That statistic makes it clear that learning how each google algorithm update works is essential to your online success. A study found that 78 percent of UK businesses adjusted their SEO approach after the December 2024 core update. Grasping both minor tweaks and major overhauls gives you a real advantage over competitors.
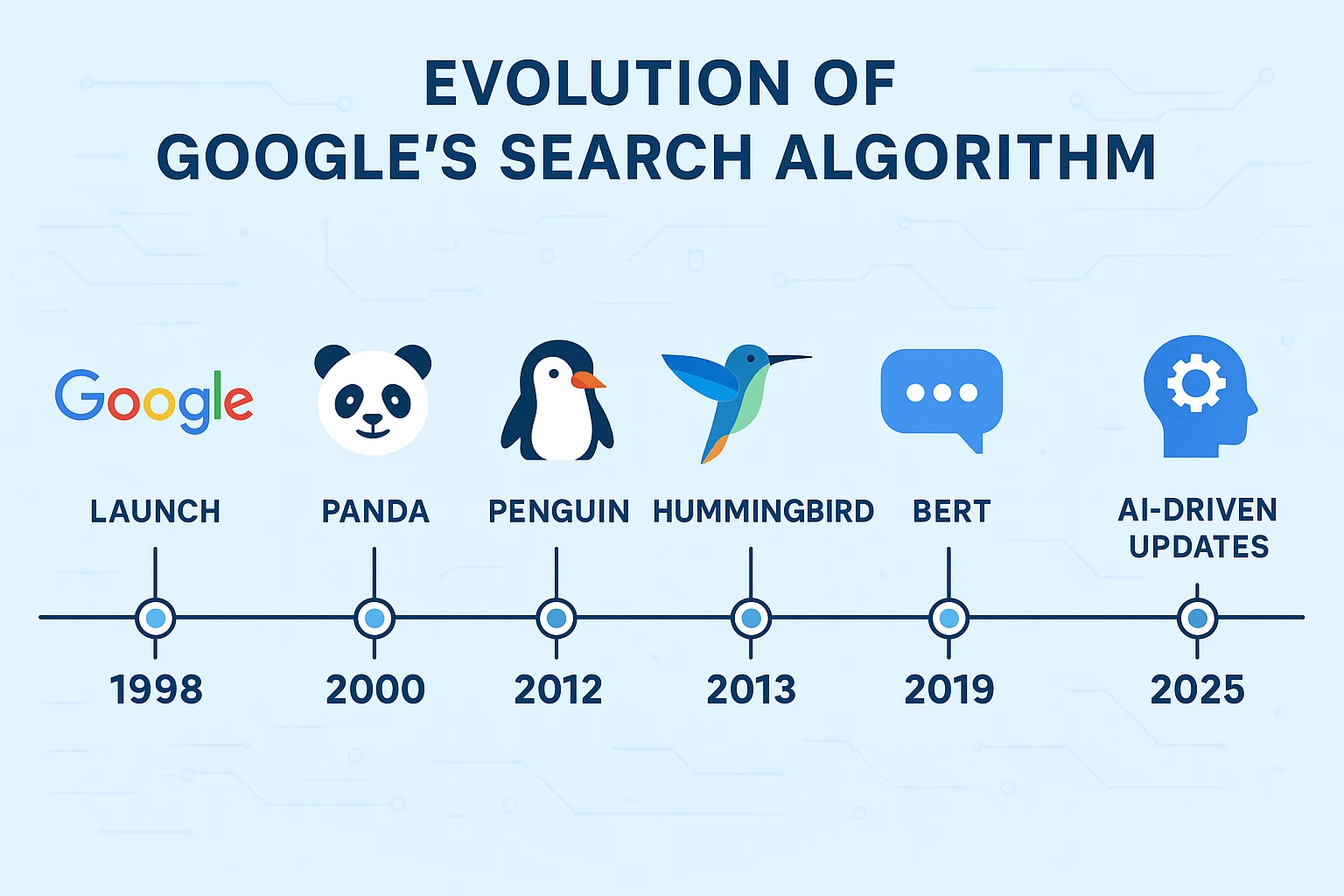
How Has Google’s Algorithm Changed Over Time?
The Evolution Timeline
| Algorithm | Launch Date | Function |
| Florida | Sep 18, 2003 | Targets thin, low-quality content. |
| Big Daddy | Sep 27, 2005 | Improves link quality assessment. |
| Jagger | Dec 18, 2006 | Penalizes keyword stuffing and link spam. |
| Vince | Feb 28, 2009 | Downgrades doorway pages and low-content sites. |
| Caffeine | Jun 18, 2010 | Enhances crawling and near-real-time indexing. |
| Panda | Feb 24, 2011 | Lowers rankings for duplicate, thin content. |
| Freshness | Nov 3, 2011 | Prioritises recently updated content. |
| Page Layout | Jan 19, 2012 | Demotes pages with excessive above-the-fold ads. |
| Venice | May 10, 2012 | Localizes search results based on location. |
| Penguin | Apr 24, 2012 | Penalizes spammy or irrelevant backlinks. |
| EMD | Sep 26, 2012 | Targets low-quality exact-match domains. |
| Payday | Aug 8, 2013 | Combats spammy finance and loan content. |
| Hummingbird | Aug 22, 2013 | Improves semantic understanding and user intent. |
| Pigeon | Jul 22, 2014 | Enhances local search accuracy. |
| Mobilegeddon | Apr 21, 2015 | Ranks mobile-friendly sites higher. |
| RankBrain | 2015 | ML system to interpret complex queries. |
| Fred | Mar 18, 2017 | Targets sites with ad-heavy, low-value content. |
| Mobile-First Index | Mar 26, 2018 | Prioritises mobile-optimized pages for indexing. |
| BERT | 2018 | Deep NLP model for context and nuance. |
| MUM | 2022 | Multitask model for complex query understanding. |
Foundations of Relevance and Rapid Indexing (2003–2010)
- Florida Update (September 2003)
Florida was Google’s first google algorithm update. Before that, many sites hid text. They used tiny fonts or matching background colors. They also built doorway pages that funneled users into low-value content. Sneaky redirects sent visitors away from the actual page. Florida taught the google algorithm to catch these tactics. It began tracking bounce rates to see if people left too fast. It also measured dwell time to check if users found what they needed. After Florida, simple writing and clear headings worked best. Webmasters removed hidden keywords and fixed redirects. Relevance and user experience became top ranking signals.
- Big Daddy Overhaul (September 2005)
Big Daddy was another google algorithm update. It rebuilt how Google crawls and indexes the web. It added URL canonicalization to the google algorithm. This change treats duplicate or near-duplicate pages as a single item. All backlinks now point to one main page. Big Daddy also improved redirect handling and DNS lookups. For example, 301 and 302 redirects now pass link credit more predictably. The update helped Google find the true source of links. Sites with real editorial mentions and high-quality backlinks gained trust. Link farms and spun directories lost their power. After Big Daddy, webmasters focused on earning genuine mentions. They turned to blogs and news sites.
- Caffeine Indexing Framework (June 2010)
The Caffeine update revolutionised the pace at which new content appeared in search results. Before Caffeine, Google’s index refreshed on a monthly schedule. After the overhaul, content flowed into search results within minutes. News sites, blogs, and event pages benefited immediately from faster visibility. Readers no longer faced delays when looking for breaking information, and publishers felt confident publishing timely updates, knowing Google would pick them up right away. This change also meant that the google algorithm began weighing freshness more heavily for queries where recent information mattered most. Content strategies shifted toward continuous updates and real-time reporting.
The Content Quality Wave (2011–2014)
- Panda Quality Score (February 2011)
Panda introduced a site-wide quality score that filtered out thin, spammy, or duplicate content. Under this change, pages with little substance or heavy ad clutter were sent to the back of the queue. Websites with in-depth articles, original research, and meaningful user engagement rose in the rankings. Panda’s checks included the ratio of useful text to HTML code and signals like time on site and bounce rate. By learning to identify real human interest, Google’s google algorithm rewarded thorough guides over brief summaries. After Panda, content creators invested in long-form articles, expert interviews, and unique visuals to build lasting authority.
- Freshness Emphasis (November 2011)
Freshness was Google’s way of telling the world that timing matters. This update examined query patterns to decide when users wanted the very latest news or when they needed stable evergreen information. For trending events, Google began prioritising pages published within hours or days. That meant a blog covering a product launch or a sudden policy change could outrank longstanding pages simply by being up to date. As a result, publishers developed editorial calendars and real-time monitoring tools. They learned that the algorithm of google search now recognized the value of timely updates, not just historic relevance.
- Penguin Link Audit (April 2012)
Penguin was a google algorithm update that cleaned up the link world. Before Penguin, many sites grew by swapping backlinks in private blog networks or buying cheap placements. Penguin made the google algorithm ignore links with exact-match anchor text or paid links from unrelated sites. When it rolled out, those sites saw their rankings fall fast. After that, webmasters hunted for honest mentions. They reached out to real blogs and earned backlinks only when they added value. In contrast, pages with natural, editorially earned links from reputable sources thrived. Google’s google algorithm rewarded organic endorsements from industry leaders, major publications, and trusted organizations. The update signaled a clear message: true authority comes from genuine connections, not from purchasing bulk links.
- Payday and Exact-Match Domain Cleanup (August 2013)
Payday and Exact-Match Domain updates tackled niche abuses in finance, gambling, and loan markets. Spammy sites built around precise keyword domains or mass-produced content found themselves buried. Google analysed query intent and content quality to demote pages that offered little more than ads or redirects. This google algorithm update forced businesses to back real expertise with clear writing. Sites could no longer rely on a catchy URL or fancy design alone. They added customer stories, FAQs, and simple menus so visitors find answers fast. They tested which headlines kept readers on the page. They made sure policies and contact info were easy to spot. In the end, search results became cleaner and safer, with quality copy and trust taking the lead.
Semantic Understanding & Mobile Revolution (2015–2018)
- Hummingbird Semantic Understanding (August 2013)
Hummingbird marked Google’s shift from mere keyword matching to true semantic comprehension. Instead of simply counting terms, the google algorithm began interpreting the intent behind a query. Google algorithm links related ideas and synonyms so you don’t have to repeat the same phrase. If you search for the best electric car charging, you could still see pages on battery technology and charging-station networks. You might also find tips on charging etiquette even when those exact words aren’t there. Content that covers the best electric car charging naturally often ranks higher. Writers can cover every angle in clear, simple language.
- Mobilegeddon Mobile-First Index (April 2015)
Mobilegeddon was Google’s message that the future is in user experience on the small screen. It made one thing clear that your site must work well on phones. Websites that did not adjust to different screen sizes or load quickly on smartphones fell in the search results for mobile queries. Google started checking how big the buttons were, how smoothly the layout adjusted, and whether content fit on the screen without sideways scrolling. In response, site owners chose themes made for phones, shrank image file sizes, and cleaned up their code to speed up loading. As more people searched by phone than by desktop, the algorithm of google search began to favour pages that made browsing easy and fast for mobile users.
- RankBrain Machine Learning Integration (October 2015)
RankBrain introduced machine learning into Google’s ranking system, letting the google algorithm learn from real user behavior. It interprets novel queries by mapping words into mathematical vectors, finding pages with similar meaning even if the exact terms differ. This approach improved results for long-tail and conversational searches. It was a google algorithm update that moved SEO experts away from chasing exact keywords and toward building topic clusters that answer real questions. Experts now focus on what people actually ask and write short, clear answers. As part of the update, pages that covered those questions naturally rose in the rankings. That change follows the google algorithm goal of giving users helpful, human-friendly results.
AI-Driven & Core-First World (2019–2025)
- BERT Contextual Language Model (October 2019)
BERT rollout lets Google read full sentences before ranking pages. This google algorithm uses deep bidirectional understanding. It looks at words before and after your search terms. It helps Google get the real meaning of your question. It says that “flights to London from New York” does not mean “flights from London to New York.” It works like reading a sentence the way a person does. It pushes pages that use everyday words and simple structure to the top. If your page answers a question in normal talk, Google sees it as helpful. Pages that jammed in tags and forced keywords dropped down.
- MUM Multitask Unified Model (2022)
In 2022, Google added MUM to its tools. This google algorithm update lets the search give text and images equal weight. It can answer a question about hiking trails based on a photo and a few words. Pages that mix clear images, captions, and plain text rose in the results. That google algorithm update set a new standard to learn across media and sees how pictures and words fit together.
Core and Spam Updates (2017–2024)
From 2017-24, Google ran core and spam updates together to keep search fair and useful. About every three months, a core update rebalanced rankings based on clear writing, real reader interest, and trusted sites. At the same time, a spam update weeded out hidden links, fake reviews, sneaky redirects, and copied text. Sites that answer real questions in simple words moved up. Sites that relied on tricks fell back. These regular updates make sure search results stay fresh, honest, and easy to use.
AI Overviews Experiment (May 2024)
Google’s AI Overviews feature began offering concise summaries at the top of certain search results, drawing on the Gemini model to condense top-ranking pages into quick bullet-style answers. Although limited to the US market, this change signals a broader move toward conversational search. To appear in these overviews, articles open with a clear summary paragraph that directly answers common user questions. Writers now craft an immediate value proposition at the start of their posts to capture attention and satisfy both human readers and automated summarisation.
2025 Core Updates (March and June)
The March 2025 Core Update rolled out over two weeks, shifting rankings based on fresh signals around expertise and reader satisfaction. Pages enriched with expert interviews, case studies, and updated statistics saw average gains of twelve percent in UK traffic. In late June, Google followed up with another core update that placed extra weight on engagement metrics like time on page and scroll depth. Search strategists responded by embedding interactive quizzes, comment sections, and multimedia elements to boost real-user interaction. These changes underscore that modern SEO relies not only on keywords but on creating content that readers truly engage with and share.
Muvera: Multi-Vector Retrieval via Fixed-Dimensional Representations
On 25, June 2025 Google introduced Muvera, a new leap in the google algorithm that puts user context and intent at the heart of every search. Muvera helps Google see what people really mean when they search, not just the exact words they type. Muvera was launched because searches have grown more detailed and varied. People no longer search in short fragments, they ask full questions, combine text with images, or expect personalised suggestions. Google needed a way to grasp all those signals at once.
Under Muvera, Google breaks each query into multiple layers of meaning such as topic, intent, and context, and matches those layers to content that satisfies every angle. It links words, images, and past behaviour in one step, so you get the most useful answer even if your phrasing doesn’t match exactly.
For SEO this means simple keyword targeting won’t cut it. The google algorithm now rewards pages that explain ideas clearly, include helpful visuals, and anticipate related questions. The algorithm of google search favours content that solves real problems over text that just repeats terms.
Example of Muvera in Action
Imagine someone searches for “best travel backpack for a 3-day business trip with a laptop under £80.” Muvera looks at four layers of meaning:
- The travel scenario (business trip)
- The item type (backpack)
- The key features (laptop compartment, 3-day capacity, budget under £80)
- The intent (buy a reliable, compact bag)
Google then shows a guide that compares backpacks by size, price, and laptop fit, even if those exact words never appear in the same paragraph.
What SEOs Should Focus On
- Write in-depth answers that cover a topic from different angles.
- Add relevant images or diagrams with concise captions.
- Use clear headings and short summaries at the start of each section.
- Blend text and visuals so every reader finds exactly what they need.
Impact on SEO Best Practices
Knowing these major updates is one thing; using them to improve your site is what really makes a difference. Today’s best approaches, shaped by years of fine-tuning, are:
- Content Quality & Depth
Google now looks for pages that cover a topic fully and clearly. Write each idea in simple words and add real examples that show you understand your subject. Link to other helpful pages on your site to guide readers deeper into the topic. Use clear headings to group related ideas and break how-to guides into easy steps. Begin each section with a question so readers know exactly what they will learn. When a page solves a visitor’s problem without extra clicks, it performs better under the google algorithm.
- Natural Link Building
Natural link building is about earning real mentions from trusted sites. Getting links from government, schools, or well-known publishers gives your site more weight. Skip bulk directory listings or shady link farms. Instead, write guest posts or team up with credible partners to earn genuine links.
- Mobile & Page Experience
People mostly browse on their phones and expect fast results. If your site takes too long or feels clumsy, visitors move on. Keep the layout clean and simple. Make text large enough to read at a glance and give buttons plenty of room for a quick tap. Test your pages on several devices to catch any problems early. A page that works smoothly on a phone earns trust from the algorithm of google search and keeps visitors engaged.
- Semantic Targeting
Use clusters of related terms, incorporate google algorithm types, what is the algorithm of google, and how google search algorithm works naturally across your text. This approach aligns with Google’s intent to reward pages that grasp the full context of a topic.
- AI-Friendly Content
As AI Overviews and MUM models grow in influence, structure your content so it can be easily parsed: clear headings (H2–H4), concise answers to common questions, and schema markup where relevant.
What’s Next for Google Search?
Updates will roll out faster and in real time. That means you need to keep improving your content all the time, not just once. Check your data in Google Search Console and refresh your main articles regularly. For an easier way to stay on top, contact Digital Lab. Digital Lab tracks your traffic trends and sends alerts when a page slips. It also suggests topics to update and shows how changes affect your rank. Start a trial at Digital Lab today and keep your site in the lead.
FAQS
What is the Google algorithm update 2025?
The June 2025 Broad Core Update is a major refresh of Google’s main ranking system. It began on June 30 2025 and will roll out worldwide over about three weeks. Instead of punishing specific sites, it tweaks many ranking signals at once to reward helpful, well-written content.
Why does Google look different today in 2025?
You’ll now see interactive summaries and chat-style panels at the top of search results. These let you expand answers or ask a quick follow-up without leaving Search. The page also highlights video, image cards, and a built-in dark-mode toggle for easier reading.
What are the changes in SEO 2025?
SEO today focuses on user experience and topic depth. Write clear, in-depth articles that cover the full context of a subject. Pay attention to mobile speed, page layout, and semantic clusters of related terms. Keep your main pages fresh by updating them often.
Has the Google algorithm changed?
Yes. Google issues broad core and spam updates every few months. These updates adjust how it ranks pages and weeds out low-value tactics. The goal is to keep search results accurate, relevant, and easy to use.